Jamstack has always been really confusing to understand for me. I can still remember the first time I heard of it, when an interviewer asked me a question related to security in Jamstack sites and I was like "What is it at the first place?". I feel one must have a decent understanding of how web works as this post is going to cover the stack to make it more efficient. 😉 Without further ado let's understand, Jamstack - The Digvijay Way!
How Websites Works?
⏩ Note, skip this section if you already know how dynamic data is loaded.
First things first, how a website works and what is static & dynamic sites? Easily guessed, static websites have static data (i.e. the data which doesn't change or is not personalized based on who is accessing it). Dynamic websites on the other hand has what we call "templates" based on some math, applications/websites shows variable values. Templates are a markup with a bunch of variables which are populated on making a requests. Refer to the below pictures to know how a template is rendered on the server side.

In the node js (express) snippet below I am making a query to my database and rendering out html templates based on the result. On the else condition (i.e. when I get the data successfully) I am passing it down as variable to my ejs template.

In the above snippet I have markup with variables embedded in it. Now I need not worry about changing it in my html files, it automatically fetches the new data upon rendering. This was the working on websites in gist for beginners. Note here, this fetch requests to a node js API/backend can be done on client side too, this was just an example.
Define It!
Jamstack stands for Javascript, API & Markup. It is an architecture which builds on top of certain workflows and practices making the web faster, more secure and easier to develop. Here,
- Javascript handles all the dynamic operations.
- API - A Jamstack application does not depends on server, instead it fetches data from APIs, serverless functions, etc.
- Markup, what is visually served to the user i.e. Html files.
Traditionally, you might have already built an application with JAM cause it's not something new. As mentioned, it's a better way of making them.
The Key Concept 📎
In the explanation above (under the topic "How Websites Works?") you might be tempted to know "Why build a page every time a client makes a request when the final result is same?" Let's say in a blog or ecommerce app, the content being loaded is consistent for any user, it changes when a new post or product is pushed in the database. So it is totally a unnecessary to build and render pages from a server increasing the load ultimately causing time and money.
This is where Jamstack comes into picture. In a Jamstack application, the request does not hit a server and generate a new html response for that specific client instead it loads up the pre-built HTML page from a CDN. In other words, every piece of dynamic content you have is turned into static HTML pages at the time of deployment or when running on your machine and is served over a CDN.
The reason we have APIs is to manage/administer and fetch the data which will then be converted into HTML pages. I will talk more about the technical flow later in this article.
At this point, what are the key benefits of all this hassle? Here we go!
- 💰 The fact that you need no expensive server spaces with more RAM, reduces costs drastically because users are going to be accessing the content from a CDN.
- ⚡ Jamstack apps are blazing fast as a client need not go through the complete hassle of making a requests to a server and waiting their html page to be generated with their desired data.
- 🚀 It is super easy to scale them! It's all on a CDN so the number of visitors don't really affects in any way.
- 🔒 You are not going to write any server side code or manage databases and since it uses APIs to fetch data, everything stays secure.
- 👨💻 It is easier and faster to develop a Jamstack application compared to other stacks. Moreover, developers gets a variety of services to choose from while planning such website.
What Are SSGs?
As I mentioned above all the dynamic content in a Jamstack application is converted into static HTML files, that is where Static Site Generators help us. If you use something like React or Vue, you might be knowing all our Javascript code is conditionally called from an HTML file. SSGs are just tools which put together the chunks of JS code in our application and generate and optimize everything into HTML pages. Fyi, they let you write code in your favorite framework, for example -
- For React - Next.js & Gatsby
- For Vue - Nuxt.js Here's a list of SSGs to choose your tool - Jamstack Generators .
Most of the SSGs caches the old builds and updates faster to add new changes made in the database, these builds are incremented with new HTML pages. Below is a snippet how Next.js plays it's role as an SSG.
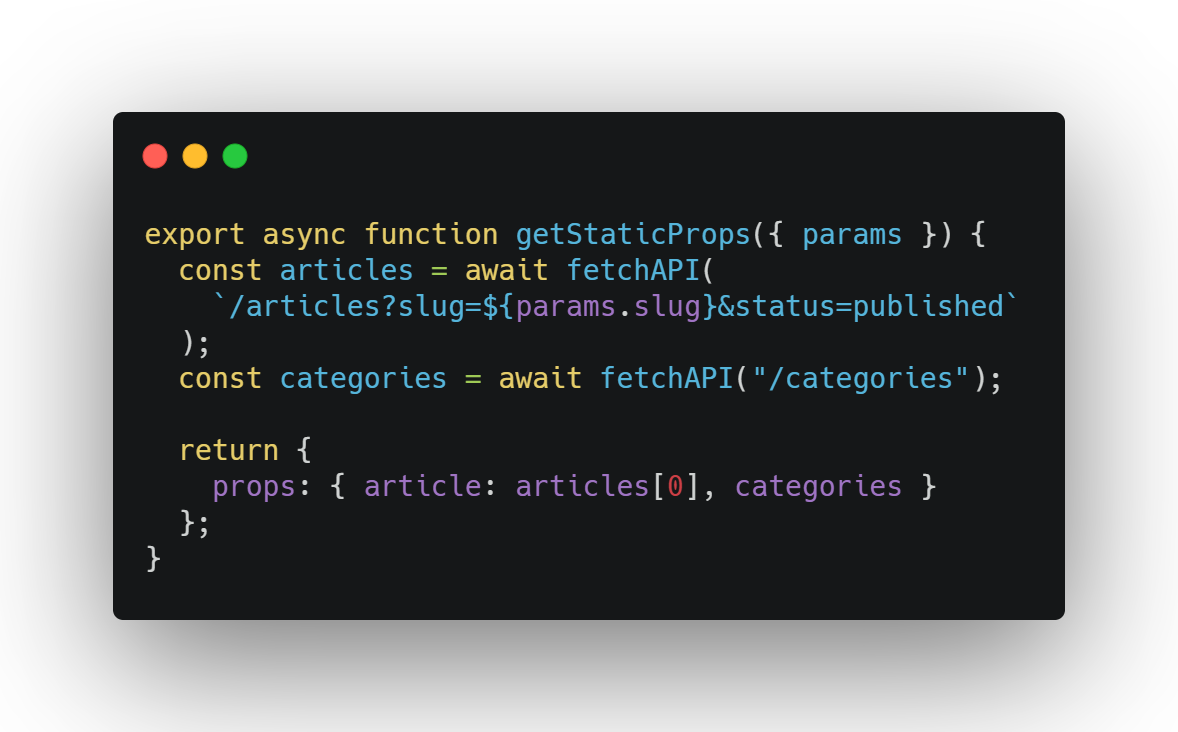
Above is a snippet to you an idea of how the data (that has to be turned into static page) is passed as props in Next.js, hopefully this makes it a little more clear.
Build Like A Pro
So now that you are finally ready to start shipping your Jamstack apps, here are a few workflows and tools you can adopt to take your Jamstacking game to the next level.
- Headless CMS - Do you want to get a cool admin dashboard to interact with your data? Introducing headless CMSs. According to the name, you get an API which can be called with any sorts of custom frontend you build. In addition to it you get an admin dashboard (all connected to your domains) if you choose a good service. Ex. Strapi, Contentful, etc.
- Vercel, Netlify & Heroku - If you are not already familiar, Vercel & Netlify are two of the best hosting services out there with very kind free tier. I have been hosting my applications since 8 months without paying anything. It's where you deploy the frontend. In case you are wondering about the API, go with Heroku!
- Tools & 3rd Party APIs - For adding extra features like forms, comments, discussion forums, etc, you can checkout plenty of free and open source tools available. In case you are building an ecommerce application, it can be done with top services like Big Commerce using their APIs so you get the privilege to use their slick admin dashboard with your custom frontend.
I am so glad you took time to read this post. Thanks! ✨
